Request An Appointment
Contact us today to request an appointment so you can start getting the sleep you need.
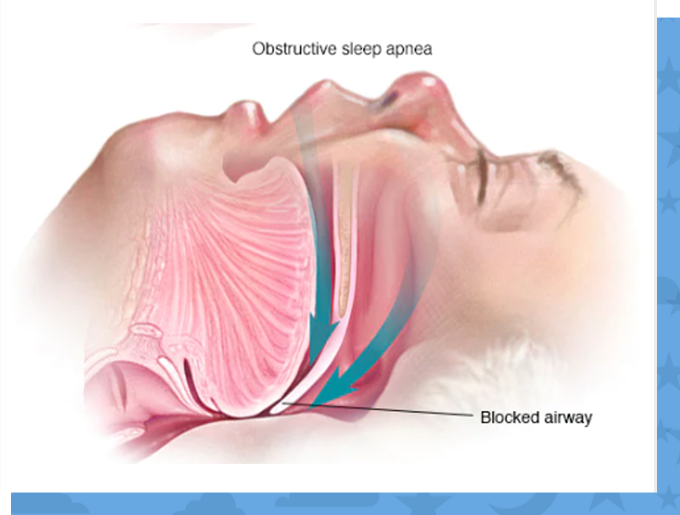
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. Each pause in breathing is called apnea – literally meaning “no breath” – and can last several seconds to a minute. When breathing is irregular, carbon dioxide builds up in the bloodstream, triggering the brain to wake the sleeping person and resume breathing.
Over 20 million Americans suffer from sleep apnea, and it’s estimated that over 80 percent of moderate and severe cases are undiagnosed.
OSA will interrupt your sleep cycle and cause common signs and symptoms.
Sleep apnea can have serious life-shortening consequences if left untreated, including:

Anyone can develop OSA, but there are certain risk factors that put you at higher potential for OSA including:
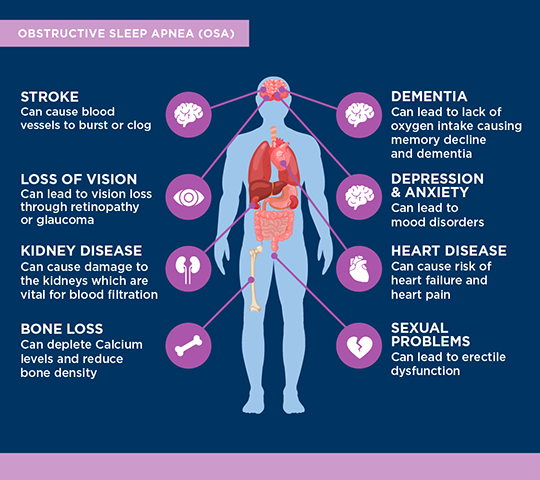
OSA is a chronic, lifelong medical condition that can affect your sleep, health, and quality of life. It has been linked to hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, work and driving related accidents, and stroke. It can place unnecessary strain on relationships between bed partners, family and in the workplace.